The ocean is unfathomable in its depth and expanse. There are untold number of species living in it and many species are yet to be discovered, still. Among them are a few that appear to be out of a horror movie, but are in fact very real.
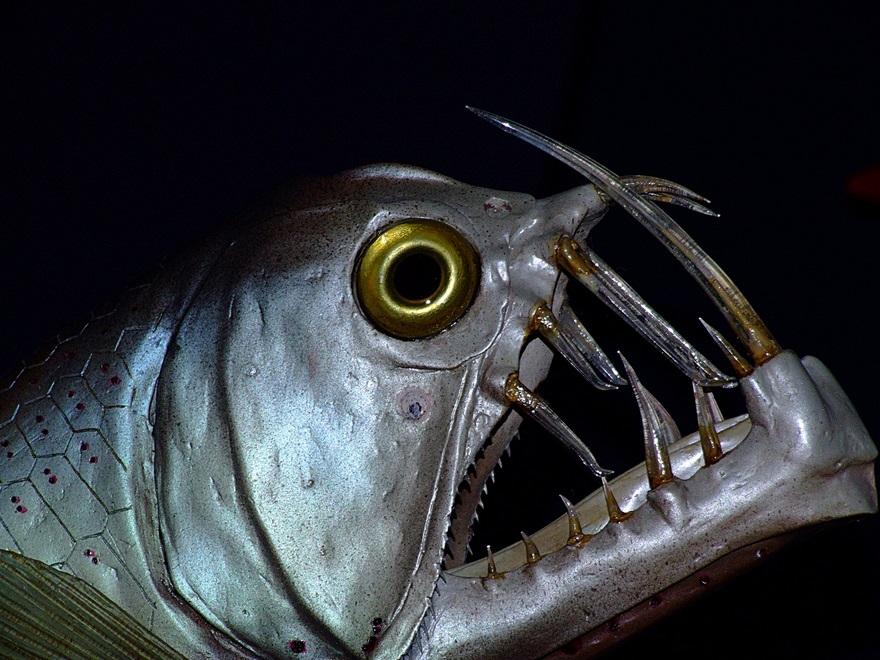
Viper Fish
Viperfish stay near lower depths (250–5,000 feet [80–1,520 m]) in the daytime and shallower depths at night, primarily in tropical and temperate waters. Viperfish are believed to attack prey after luring them within range with light-producing organs called photophores, which are located along the ventral sides of its body, and with a prominent photophore at the end of a long spine in the dorsal fin reminiscent of the illicium of the unrelated deepsea anglerfishes.
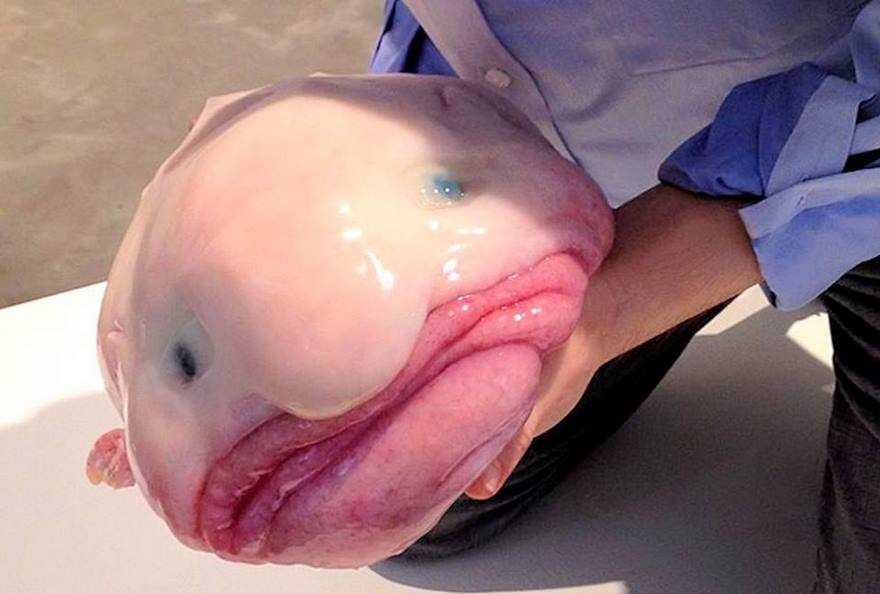
Blobfish
Blobfish inhabit the deep waters off the coasts of mainland Australia and Tasmania, as well as the waters of New Zealand. They are typically shorter than 30 cm (12 in). They live at depths between 600 and 1,200 m (2,000 and 3,900 ft) where the pressure is 60 to 120 times as great as at sea level, which would likely make gas bladders inefficient for maintaining buoyancy. Instead, the flesh of the blobfish is primarily a gelatinous mass with a density slightly less than water; this allows the fish to float above the sea floor without expending energy on swimming. Its relative lack of muscle is not a disadvantage as it primarily swallows edible matter that floats in front of it such as deep-ocean crustaceans.
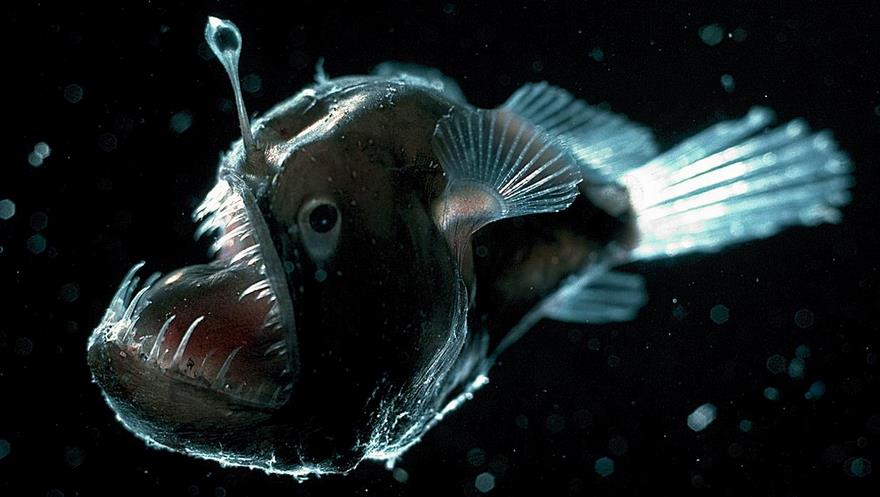
Anglerfish
They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a fleshy growth from the fish’s head (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure. Most adult female ceratioid anglerfish have a luminescent organ called the esca at the tip of a modified dorsal ray (the illicium, or “fishing rod”). The organ has been hypothesized to serve the obvious purpose of luring prey in dark, deep-sea environments, but also serves to call males’ attention to the females to facilitate mating.
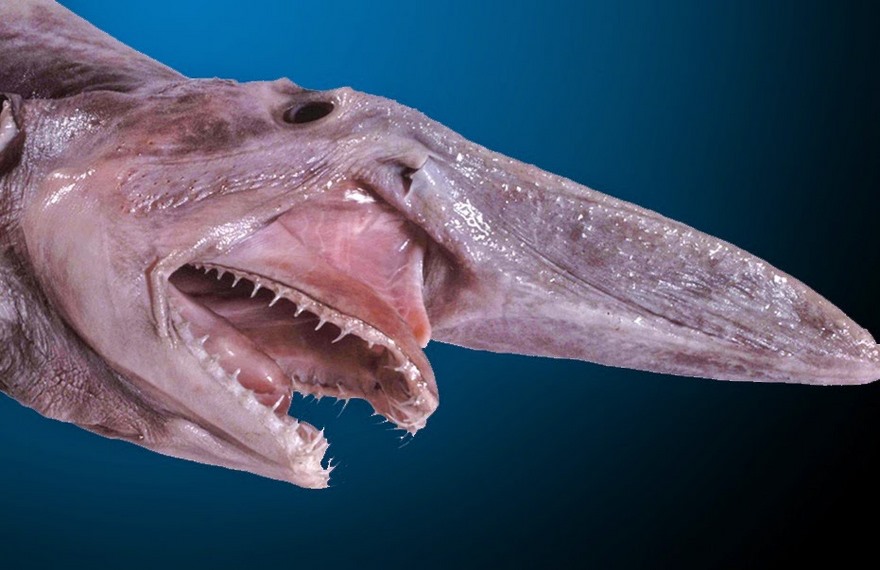
Goblin Shark
The goblin shark (Mitsukurina owstoni) is a rare species of deep-sea shark. Sometimes called a “living fossil”, it is the only extant representative of the family Mitsukurinidae, a lineage some 125 million years old. This pink-skinned animal has a distinctive profile with an elongated, flattened snout, and highly protrusible jaws containing prominent nail-like teeth. It is usually between 3 and 4 m (10 and 13 ft) long when mature, though it can grow considerably larger. Goblin sharks inhabit upper continental slopes, submarine canyons, and seamounts throughout the world at depths greater than 100 m (330 ft), with adults found deeper than juveniles.